Applying Matrix Theory in Clark Hull’s Drive Reduction Theory to analyze Learning Processes and Behavioral Responses in Educational Therapy for Students with Special Needs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64663/aet.55Keywords:
Drive Reduction Theory, ClarkHull, Hullian MatrixAbstract
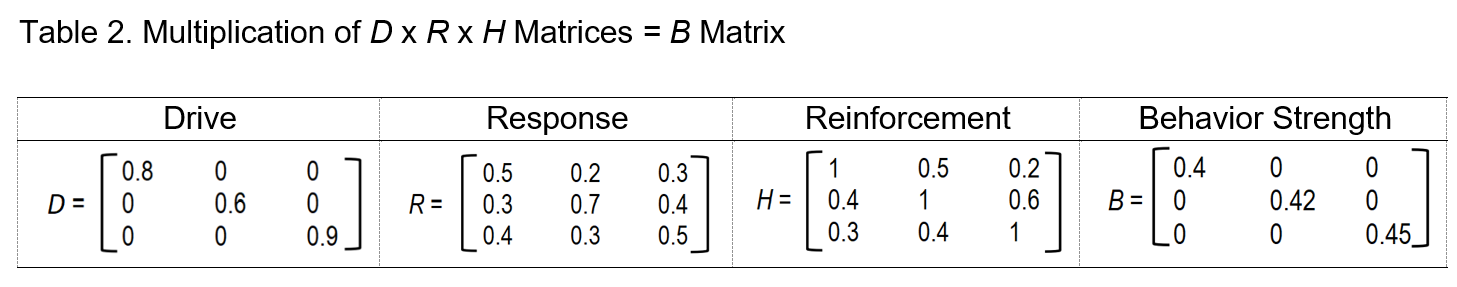
This article introduces Clark Hull’s Drive Reduction Theory (DRT), where a drive acts as a reinforcement for a specific behavior of concern, through its linear 1 x 9 equation: sEr = V x D x K x J x sHr - sIr - Ir - sOr - sLr. This Hullian equation is further expanded by applying the Matrix Theory used in linear algebra within the domain of educational therapy. This 1 x 9 Hullian matrix serves as a structured approach to understand and address students’ learning and behaviors by focusing on drives and rewards, building productive habits, and reducing barriers. Factorable causalities - autogenic, ecogenic, pedagenic, and psychosociogenic - also play their crucial roles in the drive states and learning processes that contribute to behavioral responses. With the integration of the Hullian DRT equation and Matrix Theory, educational therapists can systematically reduce behaviors driven by unmet needs, helping their students develop more adaptive responses and promoting a better learning environment.
References
Belza, B., Miyawaki, C. E., Liu, M., Aree-Ue, S., Fessel, M., Minott, K. R., & Zhang, X. (2018). A systematic review of studies using the multidimensional assessment of fatigue scale. Journal of Nursing Measurement, 26(1), 36-74. https://doi.org/10.1891/1061-3749.26.1.36 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1891/1061-3749.26.1.36
Brown, T., Almiento, L., Yu, M. L., & Bhopti, A. (2023). The Sensory Processing Measure (2nd ed.): A critical review and appraisal. Occupational Therapy In Health Care, 38(3), 842–875. https://doi.org/10.1080/07380577.2023.2280216 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07380577.2023.2280216
Camos, V., & Portrat, S. (2015). The impact of cognitive load on delayed recall. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 22, 1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0772-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0772-5
Cherry, K. (2023, August 23). Drive reduction theory and human behavior. Verywell Mind. Retrieved from: https://www.verywellmind.com/drive-reduction-theory-2795381
Chia, K. H. (2025). A proposed Hullian equation for math problem solving process. The Asian Educational Therapist, 3(2), 35-40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.64663/aet.27
Ekman, N., Taft, C., Moons, P., Mäkitalo, Å., Boström, E., & Fors, A. (2020). A state-of-the-art review of direct observation tools for assessing competency in person-centred care. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 109. Article ID: 103634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103634 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103634
Fraleigh, J. B. (1976). A first course in abstract algebra (2nd ed.). Reading, UK: Addison-Wesley.
Franklin, J. N. (2012). Matrix theory. Gloucester, MA: Courier Corporation Publishing.
How-to-ABA (2023, July 6). What are preference assessments in ABA? Retrieved from: https://howtoaba.com/preference-assessments/
Huang, F. L., Zou, G. J., Wang, L. F., He, X., Zhang, B. C., & Yang, Z. H. (2025). Open-field exploration immediately before the retention test impairs retrieval and spaced fear extinction of contextual fear memory. Behavioural Brain Research, 476. Article ID: 115260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115260 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115260
Hull, C. L. (1943). Principles of behavior. New York, NY: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Hull, C. L. (1952). A behavior system. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Hull, C. L., Hovland, C. I., Ross, R. T., Hall, M., Perkins, D. T., & Fitch, F. B. (1940). The mathematico-deductive theory of rote learning. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/2267301
Ivy, J. W., Meindl, J. N., Overley, E., & Robson, K. M. (2017). Token economy: A systematic review of procedural descriptions. Behavior Modification, 41(5), 708-737. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445517699559 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445517699559
Kahveci, G. (2016). School counseling and students with disabilities. International Online Journal of Primary Education, 5(2), 15-21.
Klein, Z., Shner‐Livne, G., Danon‐Kraun, S., Ginat‐Frolich, R., Pine, D. S., & Shechner, T. (2023). Enhanced late positive potential to conditioned threat cue during delayed extinction in anxious youth. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 65(2), 215-228. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.13814 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.13814
Koob, G. F. (2021). Drug addiction: Hyperkatifeia/negative reinforcement as a framework for medications development. Pharmacological Reviews, 73(1), 163-201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1124/pharmrev.120.000083
Lang, S. (2002). Graduate texts in mathematics: Algebra (Vol. 211; Revised 3rd ed.), New York, NY: Springer-Verlag. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-0041-0_1
Lyryx Learning & Kuttler, K. (2024). Matrix theory and linear algebra [An open text by Peter Selinger]. Calgary, Canada: The Authors.
Martin, C. (2021). Motivation in special education: Doing it differently or doing it better? Support for Learning, 36(3), 450-469. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9604.12372 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9604.12372
Merriam-Webster. (2024, October 31). Factor/Factorable. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary. Retrieved online: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/factor/factorable
Miguez, G., Laborda, M. A., & Quezada-Scholz, V. E. (2022). Clark L. Hull. In J. Vonk, & T. K. Shackelford (Eds.), Encyclopedia of animal cognition and behavior (pp. 1427-1429). Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55065-7_1231 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55065-7_1231
Montgomery, D. P., Montgomery, M., & Montgomery, M. (2023). Theories of motivation to support the needs of all learners. LEARNing Landscapes, 16(1), 213-228. Article ID: EJ1397104. DOI: https://doi.org/10.36510/learnland.v16i1.1098
Morse, W. H., & Kelleher, R. T. (2022). Determinants of reinforcement and punishment. In W. K. Honig & J. E. R. Staddon (Eds.), Handbook of operant behavior (pp. 174-200). New York, NY: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003256670 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003256670-8
Nering, E. D. (1970). Linear algebra and matrix theory (2nd ed.), New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons.
Oeri, N. (2022). Behavioral Dynamics in a Persistence Task: An Experimental Test of Persistence and Cheating during the Puzzle Box Task. Journal of Cognition and Development, 23(4), 455–463. https://doi.org/10.1080/15248372.2022.2069109 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15248372.2022.2069109
Orth, M., Aufenanger, J., Hoffmann, G., Hofmann, W., Klosson, R., Lichtinghagen, R., Otte, K., Stamminger, G., Stiegler, Y., Wiegel, B., Wieland, E. & Laboratory Medicine Section of the German Society for Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (2015). Recommendations for the frequency of ordering laboratory testing. LaboratoriumsMedizin, 38(s1). Article ID: 000010151520140045. https://doi.org/10.1515/labmed-2014-0045 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/labmed-2014-0045
Ouherrou, N., Benmarrakchi, F., Elhammoun, O., & El Kafi, J. (2018, May 7-8). The role of motivation on children with special educational needs (SEN) [Workshop presentation]. 1st TENORS’s Workshop, Chouaib Doukkali University El Jadida, Morocco. Retrieved from:
Parham, L. D., Ecker, C. L., Kuhaneck, H., Henry, D. A., & Glennon, T. J. (2021). Sensory Processing Measure, Second Edition (SPMTM-2) [Manual]. Western Psychological Services.
Pascual-Leone, A., Brasil-Neto, J. P., Valls-Solé, J., Cohen, L. G., & Hallett, M. (1992). Simple reaction time to focal transcranial magnetic stimulation. Comparison with reaction time to acoustic, visual and somatosensory stimuli. Brain, 115(Part 1), 109–122. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/115.1.109 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/115.1.109
Pins, D., & Bonnet, C. (1996). On the relation between stimulus intensity and processing time: Piéron’s law and choice reaction time. Perception & Psychophysics, 58(3), 390–400. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03206815 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03206815
Powers, S. A., & Scerbo, M. W. (2023). Examining the effect of interruptions at different breakpoints and frequencies within a task. Human Factors, 65(1), 22-36. https://doi.org/10.1177/00187208211009010 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/00187208211009010
Ray-Subramanian, C. (2013). Motivation Assessment Scale. In F. R. Volkmar (Ed.), Encyclopedia of autism spectrum disorders (pp. 1918-1920). New York, NY: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1698-3_1680 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1698-3_1680
Sandberg, M.A. (2011). Memory assessment scales. In J. S. Kreutzer, J. DeLuca, & B. Caplan (Eds.) Encyclopedia of clinical neuropsychology (pp. 1560-1561). Springer, New York, NY: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-79948-3_197 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-79948-3_197
Sehle, A., Vieten, M., Sailer, S., Mündermann, A., & Dettmers, C. (2014). Objective assessment of motor fatigue in multiple sclerosis: the Fatigue index Kliniken Schmieder (FKS). Journal of Neurology, 261, 1752-1762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7415-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7415-7
Tarver-Behring, S., & Spagna, M. E. (2004). Counseling with exceptional children. Focus on Exceptional Children, 36(8), 1-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/004005990403600501
Tarver-Behring, S., Spagna, M. E., & Sullivan, J. (1998). School counselors and full inclusion for children with special needs. Professional School Counseling, 1(3), 51-56.
Wang, T. Q, & Gao, A. X. (2025). The Hullian equation for memory process. The Asian Educational Therapist, 3(2), 30-33.
Williams, J. M. (1990). Memory assessment scales: Professional manual. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248703180_Memory_Assessment_Scales
Wu, M., Gao, Q., & Liu, Y. (2023). Exploring the effects of interruptions in different phases of complex decision-making tasks. Human Factors, 65(3), 450-481. https://doi.org/10.1177/00187208211018882 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/00187208211018882
Zhang, F. (2011). Matrix theory: Basic results and techniques. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-1099-7
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The Asian Educational Therapist

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





